Digital Health in the Circular Economy (DiCE)
EU funded project aiming to address the issue of increasing digital health waste.
Why DiCE?
Electronic waste (e-waste) from digital health devices is a complex and growing problem requiring a holistic solution. E-waste from healthcare products may pose biological or chemical contamination, leading to its incineration, with or without energy recovery. This means that all items are destroyed.
DiCE was created to bring key stakeholders together to address challenges associated with the growing use of digital healthcare products and increasing demand for raw materials to manufacture new electronic devices and other equipment.
Did you know?

E-waste in Europe
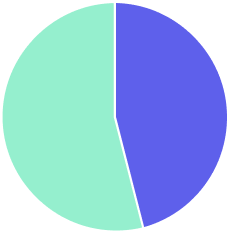
million units of medical wearables were placed on market in Europe in 2020
%
In the context of the digital transformation of healthcare, digital health device use will increase exponentially in the next decade with expected annual global growth rates of almost 20% by 2027
%
Only 54% of all electronic waste is reported as collected in Europe (compared to 17.4% globally), but rates are significantly lower for small devices and digital health devices
Project’s Scope
The DiCE collaboration involves 20 organisations from nine countries, representing the manufacturing industry, research, and recycling sectors.
A central objective of DiCE is to extend product lifetime as far as possible. DiCE will focus on testing and piloting solutions for a product’s end-of-life. The project will take into consideration circular design, state-of-the-art refurbishment, remanufacturing and recycling technology that could allow maximum recovery of the product, its components and, when reuse options are no longer available, its materials.
DiCE will thus support transition from a fragmented and linear “take-make-waste” business model towards a circular and sustainable one, allowing the reuse of products and recovery of components and raw materials.
Products in the Scope

Digital Display Label
A non-medical electronic device replacing traditional paper-based labels. These labels are mainly used on medication kits in clinical research.
Smart Wearable Sensor
A wearable sensor for patients who are discharged from the hospital. A single-use device facilitating convenient recovery at home while monitoring vital signs of the patient until necessary.
Smart Pillbox
A sensor-enabled pill box and integrated mobile application keeping track of schedules and pill types.

Endocutter
A redesigned surgical stapler used in minimally invasive and open surgical procedures such as gastrointestinal health or gynaecology.
ECG Lead Set
Connecting the electrodes on a patient’s skin to a hospital patient monitor, they are used to measure the electrical activity of the heart.

On Body Drug Delivery System (OBDS)
A device that administers high volume and/or viscous medication subcutaneously to a patient.